In the world of video games, the amazing effects we see are often due to 3D animation.
This process makes characters, places, and entire worlds come alive and feel as real as our own world.
Both creators and fans need to understand the different types of 3D game animation. The industry is so big that there are entire services for outsource animation services.

This knowledge can expand the ways stories are told, games are played, and how visually appealing they are. From very lifelike movements of game characters to the made-up settings of outer space, 3D animation comes in many styles and serves various roles in making games.
What are the Types of 3D Animation?
3D animation, in the context of game development, refers to the process of creating moving images in a digital three-dimensional environment. This technique allows creators to construct characters and scenes that can move and interact in ways that mimic real life or defy it entirely.
The versatility of 3D animation means that it can adapt to various artistic visions, from the photorealistic to the purely imaginative. The types of 3D animation covered in this exploration include:
Digital 3D Animation (CGI)
This is a method used in video games to create detailed and visually appealing characters and environments using computer software. It can make animations look very realistic or have a unique artistic style.
The power of CGI lies in its ability to construct highly realistic visuals or stylized worlds that captivate the imagination of players.
Examples of Digital 3D Animation in Games
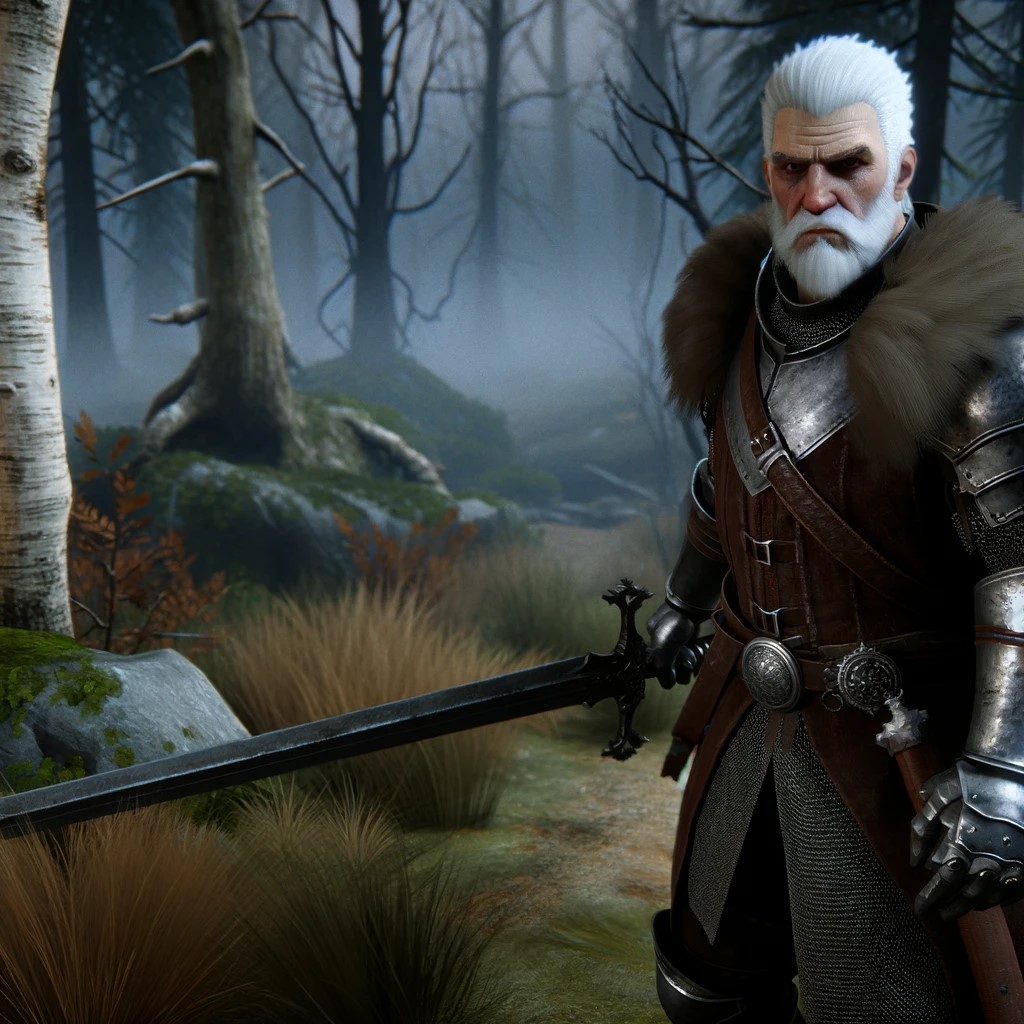

The Witcher 3: A prime example of CGI’s capability to create expansive, detailed worlds. The game’s environment and character animations are highly praised for their realism, engaging players in a vibrant, living world.
Overwatch: Blizzard Entertainment’s Overwatch utilizes CGI to bring a colorful, stylized universe to life. Character animations in this game are particularly notable for their dynamic expressions and fluid movement, illustrating the versatility of digital 3D animation to cater to different artistic visions.
Tips for Creators
Start with Solid Foundations: Before diving deep into CGI, ensure you have a strong understanding of basic animation principles like timing, spacing, and anticipation. These foundational skills are crucial for creating compelling and believable animations.
Embrace Technology: Stay updated with the latest software and technologies in 3D animation. Tools like Blender, Maya, and Unreal Engine are constantly evolving, offering new features that can enhance your animation workflow.

Interactive 3D Animation for Video Games
This kind of animation reacts to what players do. It includes styles like cartoonish for funny and exaggerated looks, fantasy for imaginative worlds, and realistic for animations that look like real life.
Interactive 3D Animation is a key feature in modern video games, making gaming experiences more engaging by letting players control and interact with the game’s world and characters in real time. This interaction is vital for game enjoyment and involvement.
Types of Interactive 3D Animation:
Cartoonish/Stylized: Games like “Fortnite” use lively and exaggerated animations to create a welcoming and fun environment that attracts many players. These animations add to the game’s light-hearted feel.
Fantasy: Games such as “Final Fantasy XV” use fantasy-style animations to make their imaginative settings feel alive. These animations help build a magical atmosphere and tell the story.
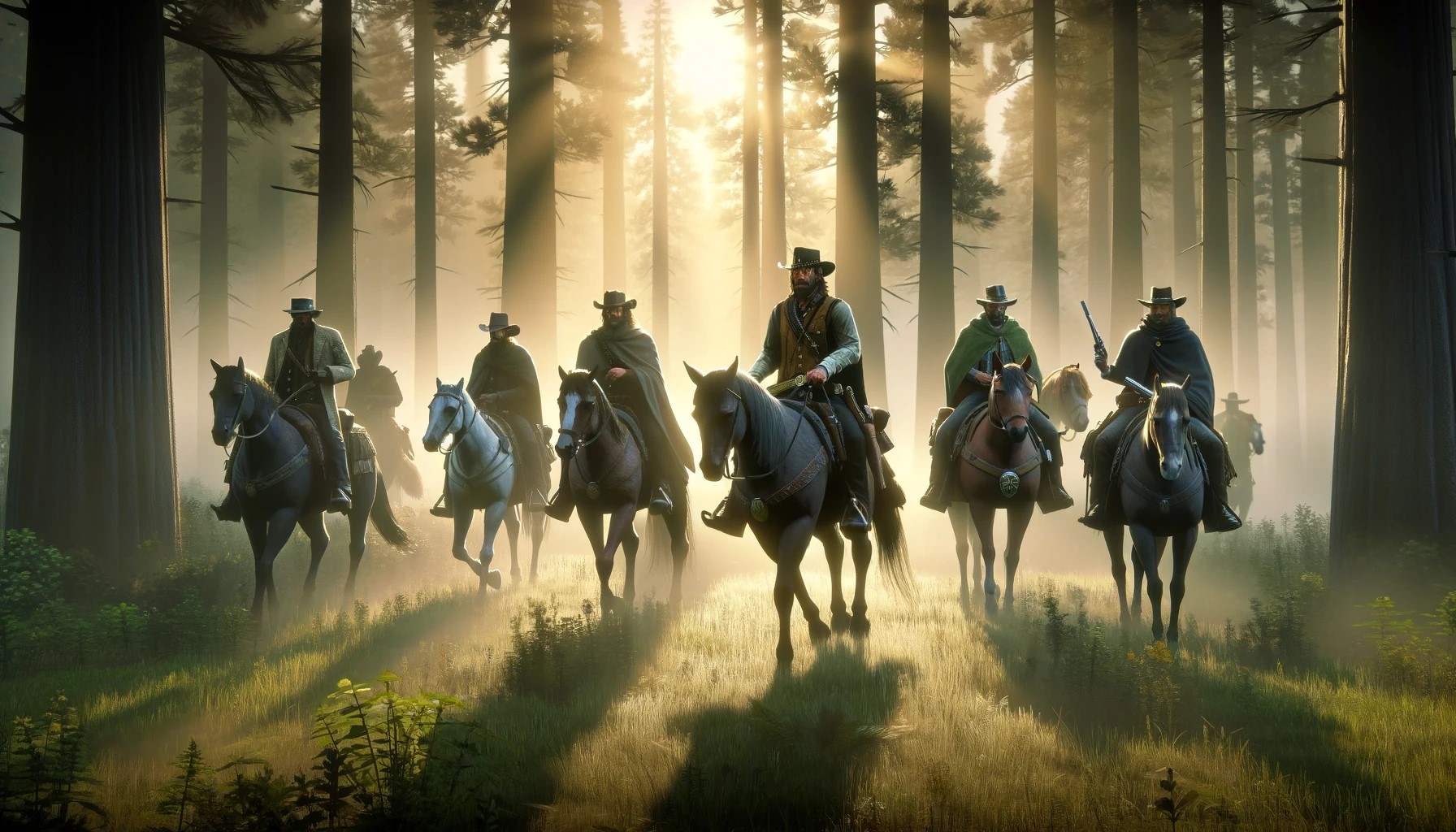
Realistic: Games that aim for a lifelike experience, like “Red Dead Redemption 2,” use animations that replicate real-world movements and interactions closely, making the game more believable.

Virtual Reality 3D Animation
VR animation takes player engagement to the next level, requiring animations that can adapt to a user’s movements and viewpoint changes, creating a fully enveloping experience.
Features of VR 3D Animation:
360-degree Interactivity: VR animations are designed to be fully interactive from all angles, offering a consistent and engaging experience for the player.
Physical Interaction: In VR, animations often have direct interactions with the player, needing accurate timing and reaction to the player’s movements.

Creating high-quality 3D assets for VR can be resource-intensive. Outsourcing companies equipped with the latest tools and technologies can produce these assets more efficiently and to a higher standard.
Stop Motion 3D Animation
A technique that blends traditional stop motion with modern 3D modeling, creating a unique, tactile feel in digital environments.
It involves capturing a series of still images of physical models or computer-generated objects, then playing them in sequence to create movement.

Characteristics of Stop Motion 3D Animation
Tactile Aesthetics: Stop motion’s charm lies in its slightly imperfect, handcrafted appearance, which can add warmth and personality to digital games.
Creative Flexibility: This style allows for a high degree of creativity, enabling animators to experiment with materials, lighting, and camera angles to achieve unique effects.
Examples of Stop Motion 3D Animation in Games
1. The Neverhood: An adventure game that stands out for its claymation technique, where every frame of animation was physically sculpted and photographed, delivering a unique, engaging player experience.
2. Armikrog: Developed by some of the same creators as The Neverhood, Armikrog utilizes similar stop motion clay animation, showcasing the potential for this technique in creating visually distinctive and memorable games.

Cel Shading (Toon Shading)
This animation style combines 3D modeling with flat shading techniques to mimic the look of hand-drawn animation.
It’s especially popular in games aiming for a comic book or cartoon aesthetic, providing a bridge between two-dimensional artistry and three-dimensional models.
Characteristics of Cel Shading
Distinctive Visual Style: Cel shading simplifies shading and highlights, resulting in a stylized, illustrative look that is immediately recognizable.
Versatility: This technique can be adapted to fit various themes and genres, from action-packed adventures to serene explorations.
Examples of Cel Shading in Games
The Legend of Zelda: Wind Waker: Nintendo’s iconic title is celebrated for its cel-shaded graphics, which have contributed to the game’s enduring popularity. The art style perfectly complements the game’s whimsical, adventurous spirit.
Borderlands series: Known for its gritty, comic book-inspired aesthetic, the Borderlands series employs cel shading to create a visually compelling world that enhances its storytelling and gameplay.

The Role of Outsourcing in Digital 3D Animation
Outsourcing animation can be a strategic move for game developers, especially for small teams or individual creators who might not have the resources to handle all aspects of game animation in-house. Partnering with specialized animation studios can bring several advantages:
Access to Expertise: Outsourcing connects you with professionals who have specific skills in 3D animation, ensuring high-quality results that might be difficult to achieve independently.
Cost Efficiency: It can be more cost-effective to outsource certain animation tasks than to hire full-time animators, especially for projects with a tight budget.
Focus on Core Development: By delegating animation work, developers can concentrate on other critical areas of game development, such as story creation, gameplay mechanics, and user experience.
When to Consider Outsourcing Animation
1. Complex Projects: For games requiring high levels of detail or sophisticated animation techniques that go beyond your team’s expertise.
2. Tight Deadlines: When your project timeline is ambitious, outsourcing can help accelerate the production process.
3. Resource Limitations: If your project lacks the necessary hardware or software for advanced 3D animation, an external studio can fill this gap.
Outsourcing isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution, and it’s essential to weigh its benefits against your project’s specific needs and constraints. However, when used judiciously, it can significantly enhance the quality and scope of your game’s animations.

Tips for Creators
When venturing into the world of 3D game animation and 3D animation art styles, creators should consider these key points:
Know Your Game’s Identity: Choose an animation style that complements the game’s theme, narrative, and desired player experience. Whether it’s the realism needed for an immersive RPG or the whimsical charm of a cel-shaded adventure, aligning the animation style with your game’s identity is crucial.
Experiment and Iterate: Don’t shy away from experimenting with different styles and techniques. Use prototypes and animation tests to find what works best for your game.
Leverage Resources: Take advantage of online tutorials, forums, and community feedback. The game development community is rich with insights and resources that can help refine your animation skills and approach.
Optimize Performance: Ensure that your animations are not only visually appealing but also optimized for performance across various devices to provide a smooth gaming experience for all players.
Future Trends in 3D Game Animation
The future of 3D game animation is poised for exciting developments, driven by technological advancements and creative innovation.
Key trends to watch include:
1. AI-Driven Animation: Artificial intelligence is starting to play a role in automating complex animations, making it easier to create realistic character movements and facial expressions.
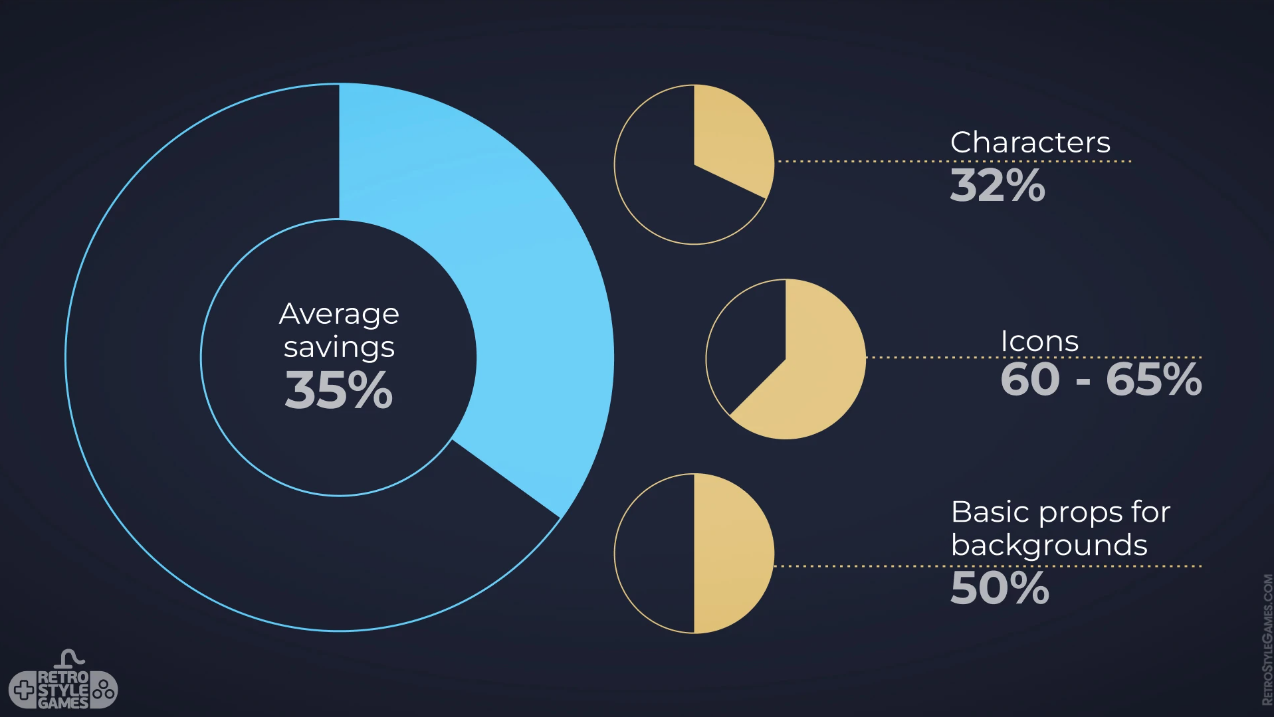
Here’s a look at an infographic from RetroStyle Games (thanks to AI tools, the average time to create in-game animations has COVERED by 35%)
2. Mixed Reality Experiences: With VR and AR technologies becoming more accessible, expect to see a rise in games that blend real-world environments with digital elements, offering new dimensions of interactivity and immersion.
3. Procedural Animation: This technique, which generates animation in real-time based on the game environment and physics, is becoming more sophisticated, allowing for more dynamic and responsive animations.
4. Emotionally Responsive Characters: Advances in motion capture and emotion detection technology will enable characters to react in real-time to players’ emotions, deepening the connection between the player and the game.




